MPFL reconstruction for Patella (Knee cap) dislocations
MPFL Reconstruction Surgery
what is patella (knee cap) dislocation?
Patella is the small rounded mobile bone that one feels in front of the knee. It normally stays well centralized over the knee and moves in a vertical direction as the knee bends and straightens.
When this knee cap moves abnormally sideways rather than in the normal vertical direction during knee movement, it dislocates from its normal trajectory causing dysfunction.
This may happen as a single incidence following a knee injury or with every movement of the knee, depending on the cause of dislocation.
what is the cause of patella dislocation or instability
There are a wide range of factors responsible for the patella to be unstable.
In sports, a direct injury or a twisting injury to the knee can cause a patella dislocation. It is more common in females and can happen even with a trivial traumatic episode. Some patellar dislocations may be present even since birth.
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) is the primary ligament responsible for keeping the patella stable. An insufficiency or tear in this ligament following injury causes the patella to be unstable. There may be multiple other factors which can be responsible for the instability. Abnormalities in the shape of underlying bone (trochlea), issues with alignment of the knee and bony structures around it, ligament and muscle strength imbalances may cause instability.
what are the symptoms of patellar dislocation or instability
what investigations are necessary to plan the management
1) Plain X-Rays of knee
2) MRI of knee
Special investigations (in some cases) :
1) CT scan knee
2) Scannogram of both lower limbs.
do all patellar dislocations require surgery
All patellar dislocations do not require surgery. Some can be treated with an initial period of immobilization followed by physiotherapy.
Some may need only arthroscopy and others may require associated mini open surgical procedures like MPFL reconstruction.
Selective cases having severe dysfunction due to multiple factors may require open surgical procedures like osteotomy or trochleoplasty(reshaping of trochlea) to restore normal bone structure of the knee.
what is mpfl
MPFL is Medial Patello-Femoral Ligament, which is the primary ligament that holds the patella in its normal position.
It is a thin, flat, fan shaped ligament on the inner aspect of knee. It spans from the knee cap to the underlying bone (femur)
what is mpfl reconstruction
When the patella dislocates, it implies that the MPFL is not functional. It may either be due to a tear in the MPFL or insufficiency with/without associated factors.
The MPFL does not heal or repair by itself if there is recurring dislocation of the patella or the instability continues. It is therefore necessary to stabilize the knee cap by recreating ie. reconstructing this ligament.
In this procedure a primary arthroscopy is performed followed by a minimally invasive reconstruction of the MPFL using ones own tissue around the knee (graft).
what is special about dr.kodkani' basket weave mpfl reconstruction
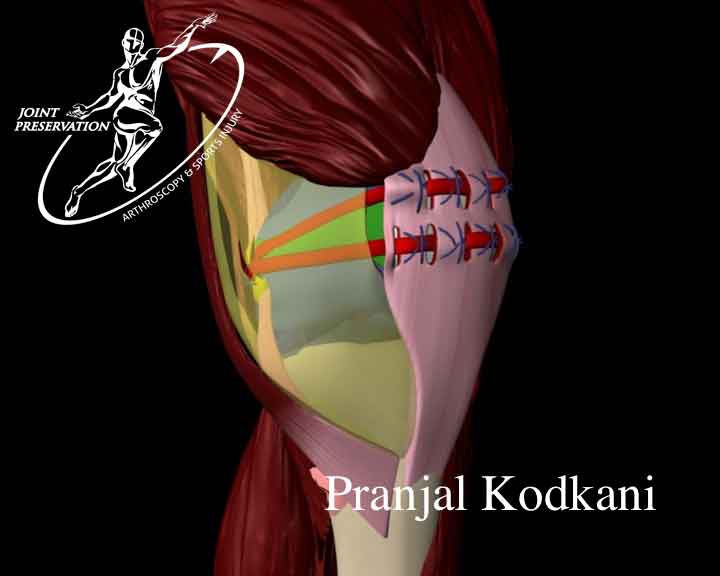 The older methods of MPFL reconstruction require artificial implants for ligament fixation, drilling and making bone tunnels in the knee cap or femur, use of radiography during surgery and at times larger incisions with use of grafts from the quadriceps tendon attached to the patella. All these older methods add to the risk in surgery and are known to give certain complications and thus compromise results. Some of these older type of reconstructions are not advisable in young children.
The older methods of MPFL reconstruction require artificial implants for ligament fixation, drilling and making bone tunnels in the knee cap or femur, use of radiography during surgery and at times larger incisions with use of grafts from the quadriceps tendon attached to the patella. All these older methods add to the risk in surgery and are known to give certain complications and thus compromise results. Some of these older type of reconstructions are not advisable in young children.
With the improvised Basket Weave technique of MPFL reconstruction all the above steps of other compromising methods of MPFL reconstruction are avoided. There are no artificial implants used, no bone drilling/tunnels performed, no intraoperative radiography and one uses the hamstring tissue as graft (with Dr.Kodkanis’ cosmetic technique of hamstring graft harvest) which is independent of the abnormally functioning patella. It is minimally invasive and a cosmetic method of reconstruction using arthroscopy. It has been proven to give better results with faster rehabilitation and least risk of any complication.
This method of reconstruction is advisable in young children.
A feeling of normalcy can be restored without the patient feeling any signs of tightness/limitation of knee movements or a feeling of reconstruction in the joint postoperatively (otherwise noted with other techniques).
what is the method for "basket weavempfl reconstruction"
A primary arthroscopy is performed
The hamstring graft (semitendinosus/gracilis) is harvested using Dr.Kodkani’ posterior mini-incision, cosmetic method of graft harvest.
Small 1-2 cm incisions are made on the knee to reconstruct the ligament from this graft. No artificial implants/ bone drilling is done and the entire reconstruction is done using special absorbable sutures only.
rehabilitation with "basket weave mpfl reconstruction"
The procedure may be performed as a day care procedure with only a single day stay.
Bracing –
1) Rigid long knee brace for upto 3 weeks
Walking –
2) Walking is permitted from day of surgery. There is no period of compulsory bed rest.
3) Use of crutches/walker till suture removal (10 days)
Knee movements –
1) Knee range of motion exercises and physiotherapy start from the day following surgery.
2) One can expect full range of motion by 1-1 1/2 month following surgery
Toning and strengthening –
1) Training for these exercises is given by the physiotherapist during the hospital stay.
2) An exercise program is tailored for sports specific training
Return to activities of daily living –
1) One is able to resume normal activities of daily living by the time of suture removal (10 days)
Return to sports –
1) 4-6 months. This depends on individual progress in recovery and the sport concerned..
The physiotherapy protocol and recovery would vary depending on any associated procedures performed in addition to an MPFL reconstruction.
