Osteotomy Knee Surgery
dome osteotomy (tibia)
Joint preservation procedures aim at restoring normal painless function to the joint by preserving native anatomy and avoiding an artificial joint replacement.
Dome osteotomy of the tibia is one such procedure which is used for management of knee osteoarthrosis (osteoarthritis) occurring as a result of degenerative knee disease.
what is osteoarthritis/osteoarthrosis?
This is a degenerative process associated with wear and tear of the cartilage (an insulating coating over the end of bones) in a joint.
In the knee, there are 3 compartments :
- Two are between the femur (thigh bone) and tibia – The medial (inner) compartment and the lateral (outer) compartment
- One between the femur and patella (knee cap) – Patello-femoral compartment
Either one or all compartments may be involved in the wear and arthritis process depending on the cause.
The commonest variety is medial compartment osteoarthritis. This is the compartment from where the arthritis commonly would start and then progress over time to affect the other compartments.
can osteoarthritis affect the young population?
Yes, osteoarthritis can affect even the young population. It is a misconception that arthritis affects only the older population. Due to various patient factors, environmental and hereditary factors, osteoarthritis has been commonly noticed in the younger population even in the early 40’s age group.
A sporting injury to the knee, if not attended to appropriately can result in early osteoarthrosis. This is commonly noticed in the sporting population.
In such young arthritic knees, a joint preservation procedure is always preferable to any kind of joint replacement.
what are the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis ?
The first symptoms are of pain in knee. The pain increases on exertion and may subside to some extent on rest. There may be swelling off and on. One may have clicking, catching and locking of knee.
As the disease progresses, one starts to have an increasing bowing of the knee. One may also find it increasingly difficult to completely extend (straighten) or fully bend the knee in later stages. Range of movement in the joint may reduce.
what are the basic investigations required ?
- X-ray of both knees in standing (weight bearing)
- Scannogram (Full length X-ray of both legs from hip to ankle) in standing
- MRI knee in selective cases
what is an osteotomy ?
This is a specialized procedure where a surgical cut is taken in the bone, primarily for a purpose of realignment. Depending on the site & type of surgical cut, method of realignment and the purpose of the procedure, various osteotomies are designed.
how does an osteotomy help in management of osteoarthritis ?
Osteotomies around the knee vary depending on the purpose for which they are performed.
The primary aim of an osteotomy is to offload the area of joint which is abnormal (arthritic). This is done by performing a surgical cut and realigning the bone. With the knee realigned, while walking there is minimal load transmitted through the abnormal area and a majority of the load is taken up by the normal unaffected area of the joint. Since minimal/no load gets transmitted through the arthritic area of knee following realignment, the knee pain & joint irritability reduces. The symptoms therefore resolve and one retains the natural structure and function of knee. This makes it an excellent joint preservation surgical option.
An osteotomy therefore rectifies the knee alignment. It corrects/overcorrects the abnormal bend in knee at the level of surgical cut. This surgical realignment offloads the abnormal arthritic area and retains all the native structures of the joint. It relieves all abnormal symptoms and obviates the need to replace any part of knee with an artificial implant.
do 'bow knees' have a correlation with arthritis ?
Bow knees are commonly noticed in arthritis. This knee deformity may also be present from ones early age. The bowing in knee causes an overloading of the medial compartment. This aggravates the medial compartment arthritis. If neglected in its early stage, it progresses in severity with further wear. It may affect the other compartments as well with a gradual increase in bowing of knee.
how early, should one undergo an osteotomy procedure ?
It is important to address medial compartment arthritis in its early stage for a joint preservation procedure like osteotomy to succeed. If it progresses to the later stages, then results of joint preservation procedures are compromised. Joint replacement would be a suitable option in situations where arthritis progresses to a severe stage.
what is dome osteotomy and how is it different from high tibial osteotomy (hto) ?
High tibial osteotomy is a generic term used for the older methods of tibial osteotomies used for treatment of knee osteoarthritis.
Realignment of the knee by taking a surgical cut in the upper end of tibia is called ‘upper tibial osteotomy’
‘Dome osteotomy’ is a special type of round cut taken in the upper part of tibia (leg bone) for its realignment unlike the standard straight cuts taken in other types of osteotomies.
This technique of osteotomy, overcomes all the disadvantages/complications of all previous types of high tibial osteotomy (HTO) and has shown to have a number of additional benefits. There is no addition or removal of any bone, no period of plastering/immobilization and allows for much faster recovery with least risk of complications.
There are no residual artificial components or implants at the end of treatment.
how is the procedure of dome osteotomy with dome stabilizer performed ?
This is a highly specialized procedure requiring specialized training and experience.
The procedure requires upto 4 days of hospital stay. One can walk back home on the 4th day with near full range of movement in the knee.
The knee joint itself remains absolutely unaltered, original, natural in the procedure and is not surgically opened. The entire procedure is carried out below the knee joint on the tibia (leg bone of knee).
Two small 1 inch skin incisions are used to perform this surgery. One in front and one on the outer side of the leg.
A small external fixator stays on the bone. It is removed without the need for any surgical incisions, on completion of treatment by 3 months. This is a day care procedure.
details of surgical method are clear in the video.
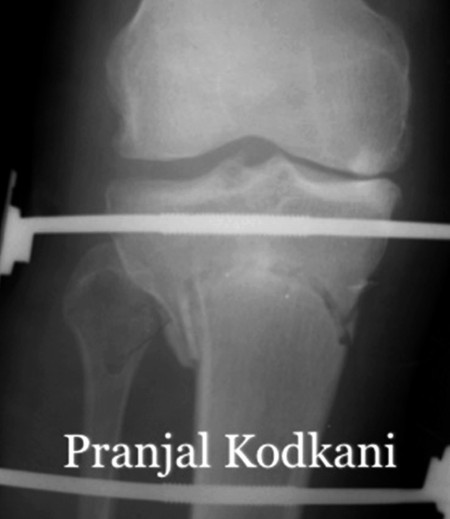
x-ray of
dome osteotomy
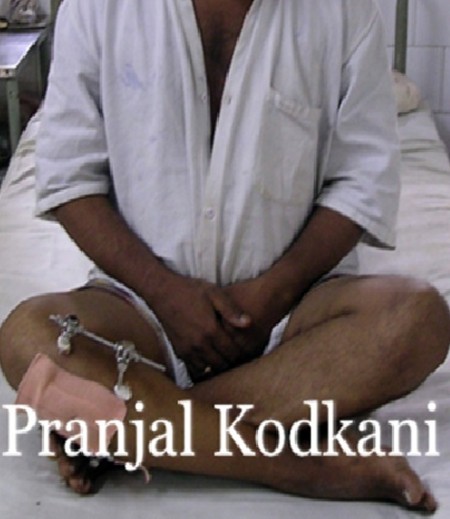
1 week after surgery
sitting comfortably cross-legged
what is the expected recovery following dome osteotomy?
- 4 days of hospitalization
- Simple physiotherapy exercises are taught during the period of hospitalization. These can be followed as home exercises without need of continuous supervision.
- Full range of motion in knee is achieved during hospitalization
- Walking partial weight bearing with support during hospitalization.
- Use of walker/support for upto 2 weeks, following which one can walk without any support.
- The external fixator needs to be kept clean till it is removed (2 1/2 to 3 months)
- Treatment completed by 3 months
are there any restrictions in activity following the procedure
- One is encouraged to perform all routine day to day activities following the procedure.
- One may limit exertion activities till suture removal (2 weeks) following which routine activities of daily living can be carried out comfortably.
- Sports can be resumed on completion of treatment at 3 months
- There is no restriction of activities due to the procedure as the original knee joint is preserved and remains unaltered. One can perform squatting and cross-leg sitting as well.
what are the other types of upper tibial osteotomies
medial open wedge osteotomy
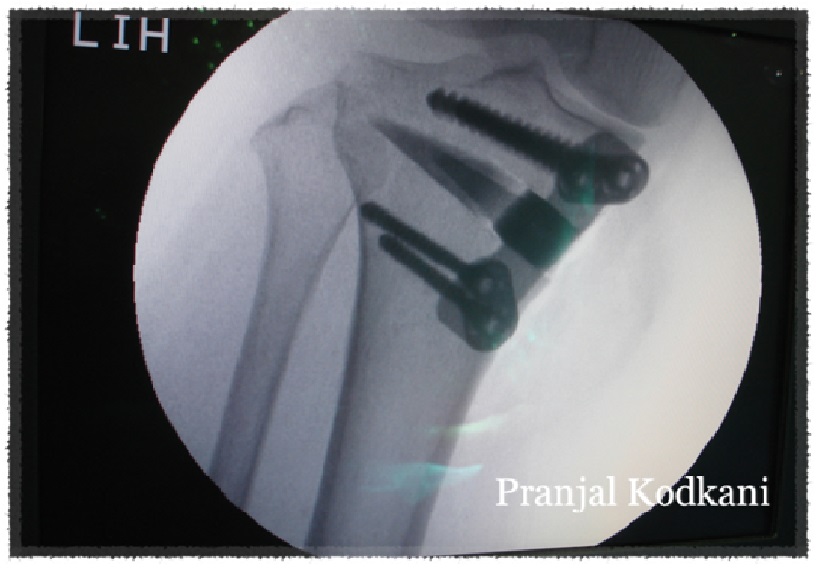 ‘Lateral closing wedge osteotomy’ was the old method of High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO). This is known to have a number of disadvantages and would require plaster immobilization of the knee. This is therefore not preferable.
A ‘reverse dome osteotomy’ is another method but requires a large ring external fixator for fixation and management. These may not be patient friendly and are cumbersome.
‘Lateral closing wedge osteotomy’ was the old method of High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO). This is known to have a number of disadvantages and would require plaster immobilization of the knee. This is therefore not preferable.
A ‘reverse dome osteotomy’ is another method but requires a large ring external fixator for fixation and management. These may not be patient friendly and are cumbersome. why should 'osteotomy' (a joint preservation procedure) be preferred to a joint replacement in osteoarthritis
An osteotomy procedure caters to all the patient’s expectations :
- One retains the original natural joint without the replacement of any part of the joint with an artificial prosthesis.
- One continues to have full range of motion in the joint and deformity is corrected.
- There is no restriction on activities following the procedure. One may even resume sports activities.
- The procedure is relatively lesser invasive and minor compared to joint replacement since the knee joint is not surgically opened or altered.
- There is the least risk of complications and no need for any revision procedure in the future. The cost of implants is also relatively lesser.
- If a joint replacement is ever required in the future, it can still be performed without any compromise due to a previous osteotomy.
