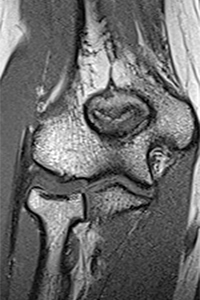
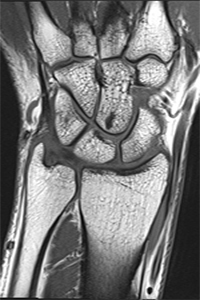
arthroscopy surgery
Joint pathologies within the confines of a joint are accessible and treatable by this most minimally invasive method of surgical treatment.
Highly specialized system of equipment is utilized to visualize the insides of a joint using a medical grade high definition camera and a tiny telescope called the “arthroscope”. State of art instruments are used to perform these specialized, precision surgeries with extreme accuracy.
Using keyhole incisions, the entire surgical procedure is carried out to rectify the pathology. Very often the procedure is entirely suture-less and performed as a day care procedure not requiring any hospitalization.
Arthroscopic, minimally invasive, precision procedures ensure reduced pain, faster recovery with better results. Expertise and specialized training of the surgeon in the procedure ensures best outcomes for the patients.
arthroscopy faq's
- Joint Inflammation in elbow, wrist, knee, or ankle.
- Shoulder arthroscopy for repairing injury to rotator cuff tendon, biceps tendon, impingement syndrome, and recurrent dislocations.
- Knee arthroscopy for meniscus or cartilage tears, chondromalacia, etc.
- Wrist arthroscopy for repairing torn cartilage or loose bodies.
- Repair loose bone or cartilage.
At first, the surgeon examines the joints. Then, the surgeon makes small stab incisions on the joints to expose and examine them from different angles and insert or pass surgical tools.
Next, the surgeon inserts an arthroscope to view the internal joint surface and plan the surgery. Finally, the surgeon will fill the joint with sterile liquid to help visualize the joint clearly.
Then, the surgeon inserts precision tools through button hole channels called portals and operate, cut, shave and trim the cartilage and bone spurs at joints to reduce inflammation and restore functionality.
Finally, the surgeons withdraw tools, check the joint’s mobility, and close the incision after irrigating it with a sterile solution.
The doctor will prescribe medications and therapies for post-surgery joint rehabilitation.
- Used for detailed diagnosis
- Requires small incisions
- Less soft tissue damage
- Less post-surgical pain
- Faster healing
- Lesser recovery time
- Lower infection rate
- Improved joint mobility
- A joint replacement preventive procedure
- Knee arthroscopy
- Hip arthroscopy
- Shoulder arthroscopy
- Elbow arthroscopy
- Wrist arthroscopy
- Ankle arthroscopy
- Partial Meniscectomy or removal of a torn meniscus
- Meniscal Repair, transplant
- Removal and repair of loose fragments, cysts
- Trimming and smoothening of joint-surfaces
- Cartilage surgery
- Synovectomy: removal of the inflamed joint lining
- Patella ligament reconstruction
- Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
- Osteoarthritis
- Treating infections
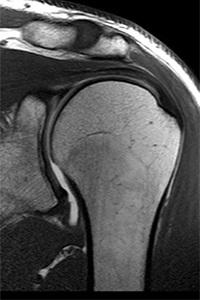
The shoulder arthroscopy is the procedure by which the surgeon inserts the arthroscope into thin incisions and sees shoulder joints and surrounding parts comprising ligament, rotator cuff, and tendons. Then, the surgeon diagnoses and treats the shoulder joints accordingly.
Shoulder arthroscopy is done in the administration of general anesthesia. After this, the surgeon makes small stab incisions to insert the endoscope and other precisional instruments. Next, the surgeon locates, trims, repairs, or resurfaces the joint and checks for mobility and stability. Finally, the surgeon closes the incision with dissolvable sutures.
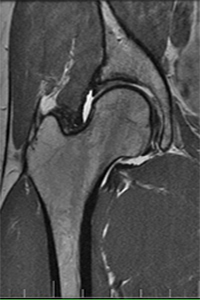
Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure done to treat the hip joint. The hip joint is a ball socket joint that joins the pelvic bone to the femur or thighbone. It is also an important junction of the upper to lower body.
First, the surgeon sedates the hip joint. Next, the surgeon makes one or more key-hole incisions at appropriate sites to access the hip joint smoothly.
The surgeon inserts guidewire, cannula, and arthroscope through the keyhole portal. The surgeon also exchanges surgical tools through these portals.
After examining the hip- joint through arthroscope, the surgeon inserts retractors, clasp, and trimming instruments to shave, trim and repair, bone spurs or articular damage. Once the surface is smoothened, the joint mobility is checked, and the instruments are withdrawn.
Finally, the incision is closed with sutures, and the patient is released with post-surgical instructions and precautions.
- The swollen or abnormal femoral head
- Acetabulum abnormalities
- Labral tears
- Ligament tear
- Bone spur
- Stabilizing hip-joint by inserting bone graft
- Temporary nerve impingement during and after the procedure.
- Hip traction and
- Infection risk (very rare)